The Tertiary Structure of a Protein Is the _____.
Amino acid side chains may interact and bond in a number of ways. - Voiceover In the video on protein structure we talked about the different orders of structure starting with primary structure and this is all a bit of a review right now.

Biology In Focus Chapter 3 Review Flashcards Quizlet
Tertiary structure is the three-dimensional shape of the protein determined by regions stabilized by interactions between the side chains.

. The three-dimensional shape of a protein its tertiary structure is determined by the interactions of side chains from the polypeptide backbone. This is what we call the tertiary structure of proteins. Make sure you know the secondary structures that make up the tertiary structures.
KERATIN IS MADE UP OF TWO RIGHT HANDED HELICES BUT IT MAKES A LEFT HANDED COIL. Quaternary structure is the association between two or more polypeptides but not every protein has a quaternary structure. The quaternary structure also influences the three-dimensional shape of the protein and is formed through the side-chain interactions between two or more polypeptides.
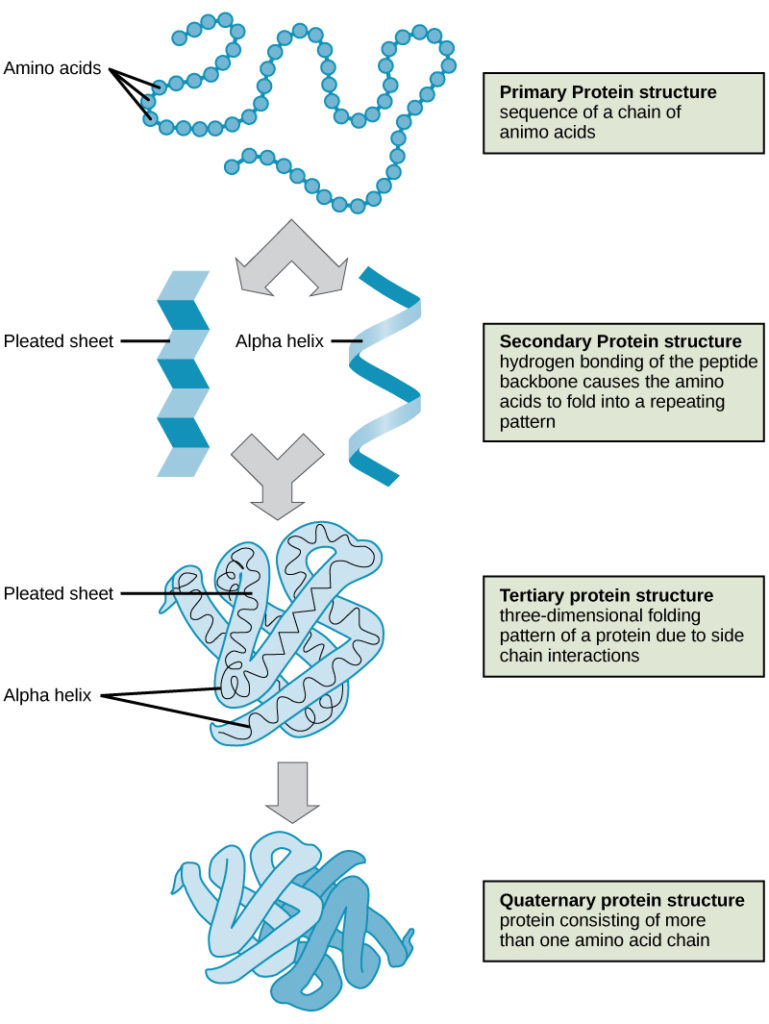
Generally the information for protein structure is contained within the amino acid sequence of the protein itself. The tertiary structure of a protein is the three-dimensional shape. The simplest level of protein structure primary structure is simply the sequence of amino acids in a polypeptide chain.
The filled circles at the top are amino acids that bind to the antigen Most of the secondary structure of this protein consists of beta. Hydrophobic interactions greatly contribute to the folding and shaping of a protein. Tertiary structure the three-dimensional structure of a proteinis the next level of complexity in protein folding.
This final shape is determined by a variety of bonding interactions between the side chains on the amino acids. Each circle represents an alpha carbonin one of the two polypeptide chains that make up this protein. They are strongly influenced by side chain groups.
The insulin molecule shown here is cow insulin although its structure is similar to that of human insulin. Driving force for protein folding. Tertiary Structure refers to the comprehensive 3-D structure of the polypeptide chain of a protein.
For example the hormone insulin has two polypeptide chains A and B shown in diagram below. Protein tertiary structure is the three dimensional shape of a proteinThe tertiary structure will have a single polypeptide chain backbone with one or more protein secondary structures the protein domains. Keratin two right handed coils to make a left.
Whereas individual amino acids in the primary sequence can interact with one another to form secondary structures such as helices and sheets and individual amino acids from distant parts of the primary sequence can intermingle via. Unfolded proteins cause H20 water cages which are very unfavorable. Generally the information for protein structure is contained within the amino acid sequence of the protein itself.
The primary structure is simply the order of the amino acids in the polypeptide chain. Primary structure is just a sequence of the amino acids. Tertiary structure is the three-dimensional shape of the protein determined by regions stabilized by interactions between the side chains.
The tertiary structure of protein definition is the arrangement of amino acid side chains in the protein. There are several types of bonds and forces that hold a protein in its tertiary structure. A protein can have one or more domains.
Tertiary structure is the next level up from the secondary structure and is the particular three-dimensional arrangement of all the amino acids in a single polypeptide chain. This important principle of biochemistry was first determined by the biochemist Christian Anfinsen in studies of the enzyme ribonuclease. The interactions and bonds of side chains within a particular protein determine its tertiary structure.
The tertiary structure is the final specific geometric shape that a protein assumes. These bonding interactions may be stronger than the hydrogen bonds between amide groups holding the helical structure. This is the structure that gives protein the 3-D shape and formation.
These are both local structures. Fibrous mainly 4 types. They are usually stable but do not conform to any frequently recurring pattern.
Free energy from removal of what compound from water. After the amino acids form bonds secondary structure and shapes like helices and sheets the structure can coil or fold at random. The interactions and bonds of side chains within a particular protein determine its tertiary structure.
The tertiary structure is created by several types of bonds between the amino acids. Davies represent the tertiary structure of the antigen-binding portion of an antibody molecule. This important principle of biochemistry was first determined by the biochemist Christian Anfinsen in studies of the enzyme Ribonuclease.
The R group of the amino acid is either hydrophobic or hydrophilic. Is the number and arrangement of multiple folded protein subunits in a multi-subunit complex. The tertiary structure of a protein refers to the arrangement of amino acid side chains in the protein.
Quaternary structure is the association between two or more polypeptides but not every protein has a quaternary structure1234 Nearly every function in living beings depends on proteins. But then from there we can start thinking about how does it get shaped by thinking about the secondary structure. The images courtesy of Dr.
Amino acid side chains may interact and bond in a number of ways. Protein tertiary structure is the three dimensional shape of a proteinThe tertiary structure will have a single polypeptide chain backbone with one or more protein secondary structures the protein domains. Tertiary structures involve packaging the secondary structures into compact globular regions called protein domains.
Used mainly of a protein to refer to its three-dimensional folded shape in space. This structure is usually conformational native and active and is held together by.

Foundations Week 1 Amino Acids Flashcards Quizlet
Protein Structure Biology For Non Majors I

Solved The Sequence Of Amino Acids Is Called The Chegg Com

Chapter 3 Proteins Flashcards Quizlet
Solved Assignment 7016434 Chegg Com

Biol101 Masteringbiology Ch 3 Flashcards Quizlet

Protein Structure And Function Relationships Flashcards Quizlet

Biol101 Masteringbiology Ch 3 Flashcards Quizlet

Microbiology Mastering Microbiology Homework Chapter 2 Diagram Quizlet
Comments
Post a Comment